The Leading Manufacturer of
Friction Hinges and Torque Hinges
Torque Hinge Reference Guide
Torque hinges are a type of specialty hinge used in applications that require precise control of panel position with smooth controlled movement. They are unique since they provide consistent resistance across their range of motion. Torque hinges are essential components found in many applications today ranging from laptop screen displays to industrial equipment covers.

What is a Torque Hinge?
A torque hinge is a mechanical device that provides rotational resistance while allowing smooth motion between two connected components. While regular hinges only pivot freely, a torque hinge applies an equal opposing force throughout its full range of motion. This resistance provides what’s known as “positioning torque” – the ability to hold a panel, lid, screen, door, etc. at any specific position without additional support devices.
The most important feature that distinguishes torque hinges from other hinges is their capacity to ensure constant torque output regardless of the angle of rotation. Let’s look at a laptop screen as an example. Whether you position it at 45° degrees or 135°, the hinge holds the screen in place by providing the same level of resistance.
How are Torque Hinges Different from Other Hinges?
Traditional hinges provide free movement. This allows the lid, door or other hinged component to swing freely with minimal resistance. Examples of these are everywhere and include butt hinges, piano hinges, and strap hinges. Simply put, they are designed for any application that allows rotation with the assistance of the weight of the moving element.
Conversely, torque hinges do not provide free movement but controlled resistance. This is due to the fact that they have a more complex design. They are composed of various components like friction discs, springs, or dampening systems that provide predictable resistance to motion.
Torque Hinge Applications
 Torque hinges are found in an extensive range of industries and applications, which include:
Torque hinges are found in an extensive range of industries and applications, which include:
- Electronics – torque hinges are a necessity in laptops, tablets, and consoles where smooth screen motion and exact positioning are crucial.
- Medical – torque hinges are often applied to adjustable monitor arms, examination lights, and equipment covers that need to stay in position during procedures.
- Industrial – applications include machinery guards, control panel enclosures, and equipment doors. These are uses where consistent positioning is needed without the added complication of other locking mechanisms.
- Auto – Torque hinges are found in dashboard screens, console lids, glove boxes, and specialty automotive applications where smooth controlled motion is needed.
Materials
The requirements of the application ultimately determine the materials used for torque hinges. Let’s examine a few:
Stainless steel torque hinges are popular due to their resistance to corrosion and longevity, making them ideal for marine and medical applications. Stainless steel’s has also has an excellent strength-to-weight ratio which makes it a great material choice for heavy-duty industrial uses.
Aluminum torque hinges weigh lighter than steel, but without sacrificing strength. They are often found in aerospace and portable electronics – two industries where weight reduction is critical.
Because of their superior corrosion resistance and inherent lubricating qualities, brass and bronze torque hinges are suitable for both low-maintenance and outdoor applications. For architectural applications, the materials also offer durability and a beautiful appearance.
Torque hinges are constructed from special alloys for high temperatures or exotic titanium for aerospace applications.
Choosing the Right Torque Hinge
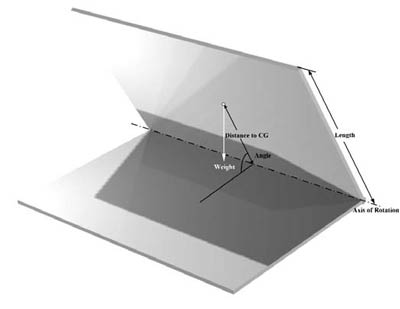 Design engineers have to consider several factors when specifying a torque hinge for a specific application. The first one, and it’s a big one, is to determine the required torque value. The torque value is based on the moving element’s weight and center of gravity. Both dynamic torque for frictionless motion and static holding torque for position keeping must be considered.
Design engineers have to consider several factors when specifying a torque hinge for a specific application. The first one, and it’s a big one, is to determine the required torque value. The torque value is based on the moving element’s weight and center of gravity. Both dynamic torque for frictionless motion and static holding torque for position keeping must be considered.
Material selection is heavily influenced by environmental conditions. Key factors such as temperature range, humidity, chemical or UV exposure all impact material and finish selection.
The degree of movement needed is another key hinge design consideration. Some applications demand 90-degree movement, while others demand 180 degrees or more. Space requirements are another key factor. Torque hinges can be made in a variety of sizes and designs to accommodate various spacing requirements – from extremely tight, to those that are more forgiving.
Load computations must take into account not only the static load, but any dynamic loads that are supported during operation. Wind loads on external applications, user action forces, and impact loads are all factors that come into play during the specifying process.
Alternatives to Torque Hinges
There are several options to using torque hinges, each has some benefits as well as drawbacks.
- Gas struts – provide support by position but tend to perform best in vertical application and can deteriorate over time. They also provide variable resistance with position, which can be suitable or not suitable for all applications.
- Friction stays – possess some positioning capacity but provide less predictable resistance than torque hinges. Stays are better suited for lighter loads and less demanding applications.
- Traditional hinges with locking mechanisms provide positioning control, but are unnecessarily complex. This complexity can also lead to failure points. They are also a bit of a nuisance to use, as they requires the user to lock and unlock the mechanism.
- Ball detents and magnetic catches can also provide fixed angle positioning but they do not supply the infinite positioning that a torque hinge does. They are better suited where discrete and non- constant adjustment is required.
Maintenance
Quality torque hinges are designed for years of reliable service with very minimal maintenance. Regular inspection and greasing can extend their life considerably, though. In harsh conditions, more frequent servicing and cleaning may be necessary to ensure consistent, reliable operation.
The internal mechanism that provides torque resistance can degrade over time, and the holding force is then gradually reduced. It’s important for engineers to be aware of this possibility, and make design, material and other choices accordingly – especially for mission- and safety-critical applications.
Conclusion
Torque hinges are ideal for applications that require both controlled motion and precise positioning. Their ability to provide consistent resistance throughout their range of motion makes them invaluable to industries ranging from electronics to heavy machinery. When properly specified and maintained, a torque hinge can provide years of trouble-free operation, and as such, it represents an investment worth considering where controlled movement is critical.
Understanding the unique characteristics of torque hinges and how they differ from other positioning solutions will allow engineers to make informed choices that have a positive impact on product performance and user experience. Whether you are designing the next generation of portable electronics or rugged industrial or defense devices, torque hinges offer the precision and reliability applications demand today.
